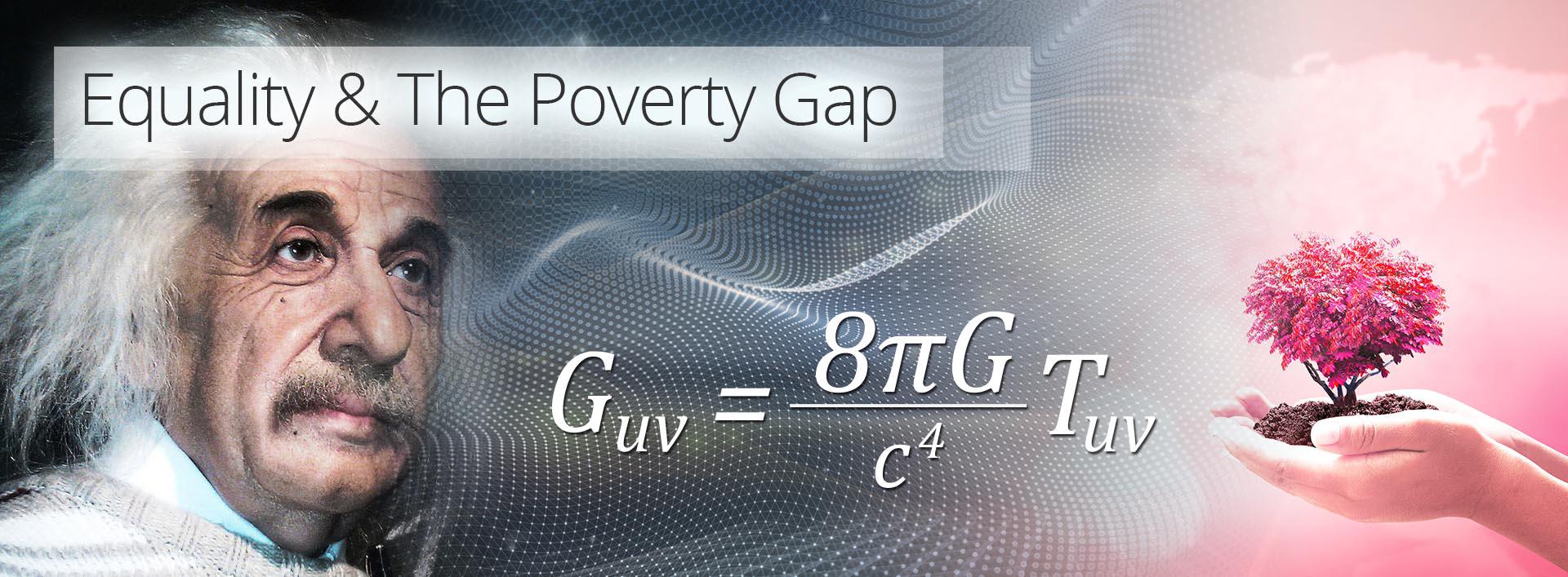
Relative Equality
Angel Theory – Paradigm Shift: Book 2.
Backstory / Prequel
An Economic Theory of Everything
By Nick Ray Ball 19th November 2017

PRESENTING:
Chapter 2 Part 6: Relative Equality
An Economic Theory of Everything Part 6: Einstein’s theory of gravity simulated as a theory of equality as we grow those mountains and fill them valleys!
Inspired by Sienna Skye
In 1,261 Words
Version 6.59-6r
Step 16. Relativity (Space, Time & Gravity)
Before we begin this final step, please note on the graphic below the question marks above and below Step 16. ‘Relativity.’
At the point of making the graphic (in August 2017), this step was in place for others to contribute to, as I knew little relativity and had nothing significant to add in terms of economic simulations.
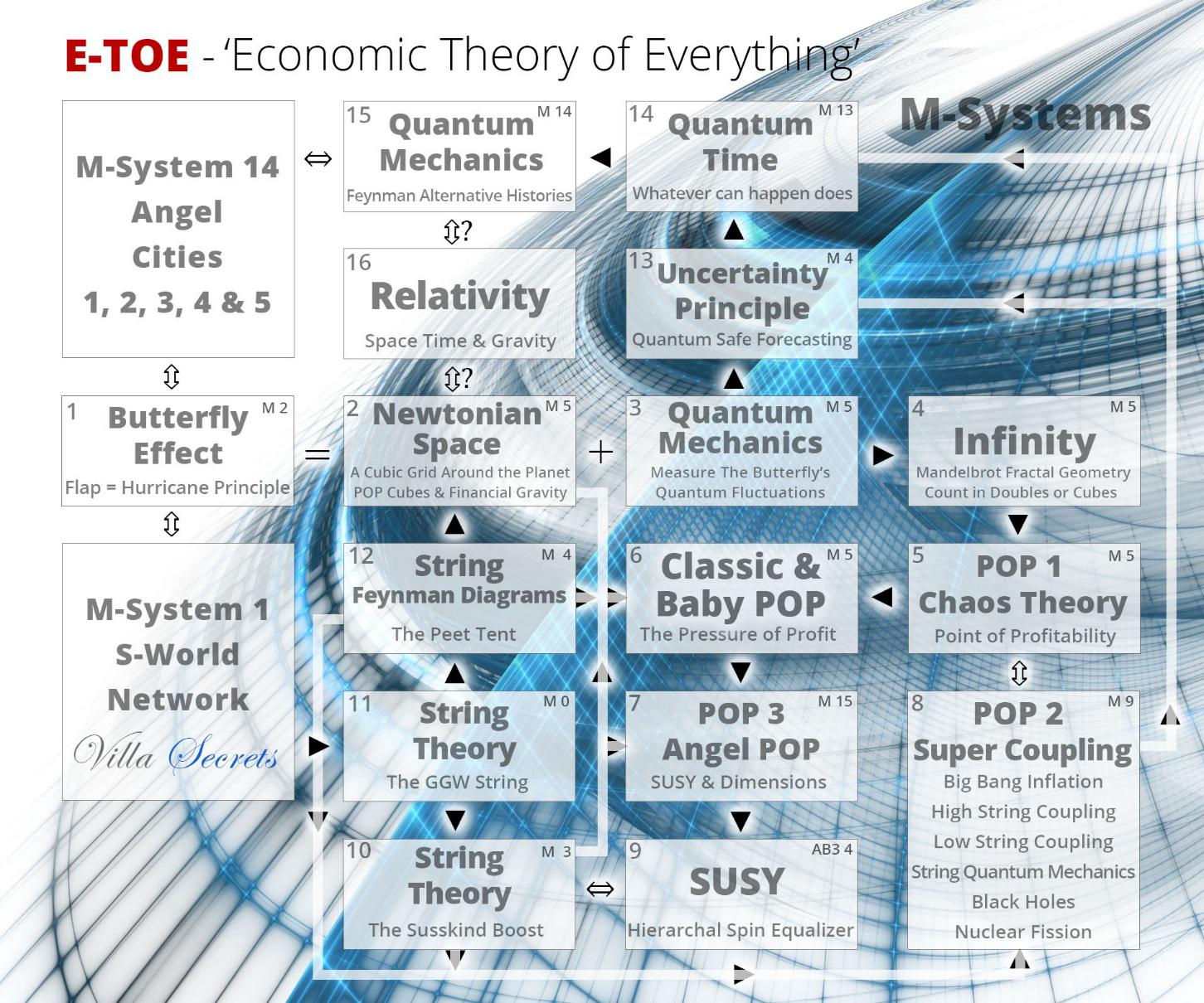
However, as it turned out, I found some time to study. And whilst we are only starting to add systems within the E-TOE, I think in terms of the idea that one can use qualities of M-theory to create an economic system in the first place are better made from relativity than any other perspective.
By creating a system inspired by quantum mechanics, string theory, supersymmetry and M-theory, it’s a testament to the accuracy of the simulation when just like Professor Edward Witten tells, out pops general relativity for free.
Albeit, in our case, special relativity popped out for free.

Step 16 Part 1. Einstein’s Theory of Special Relativity (1905)
In 1905, Einstein proposed his theory of special relativity and the idea that time and space are two sides of the same coin, which when pictured mentally could be visualised in a similar fashion to the original cubic grid around the butterfly from E-TOE Steps 1, 2 & 3 from the summer of 2011.

Despite no definite plan, Angel Theory’s M-Systems are brimming with special relativity; as, at the heart of special relativity, ‘time and space are the same and interchangeable
Starting with Time…
In the past 2 Quantum steps, we have seen ‘time.’
In Step 14, we create a virtual copy of our business network and pushed it forward in time, and let business benefit from the foresight back in real time, creating economic time travel.

Then in Step 15. ‘Angel Cities,’ we create 5 points in the future (2020, 2024, 2032, 2048 & 2080) where after the billions of opportunities and even more ripple effects are created (back and forth from 2080 to 2020) that govern the development of the network and our ecological economy.
Via S-World UCS Voyagers and Angel Cities, we make very precise and incredibly flexible plans to creating the Utopian Angel City 5 (2080) idea of a perfect future.
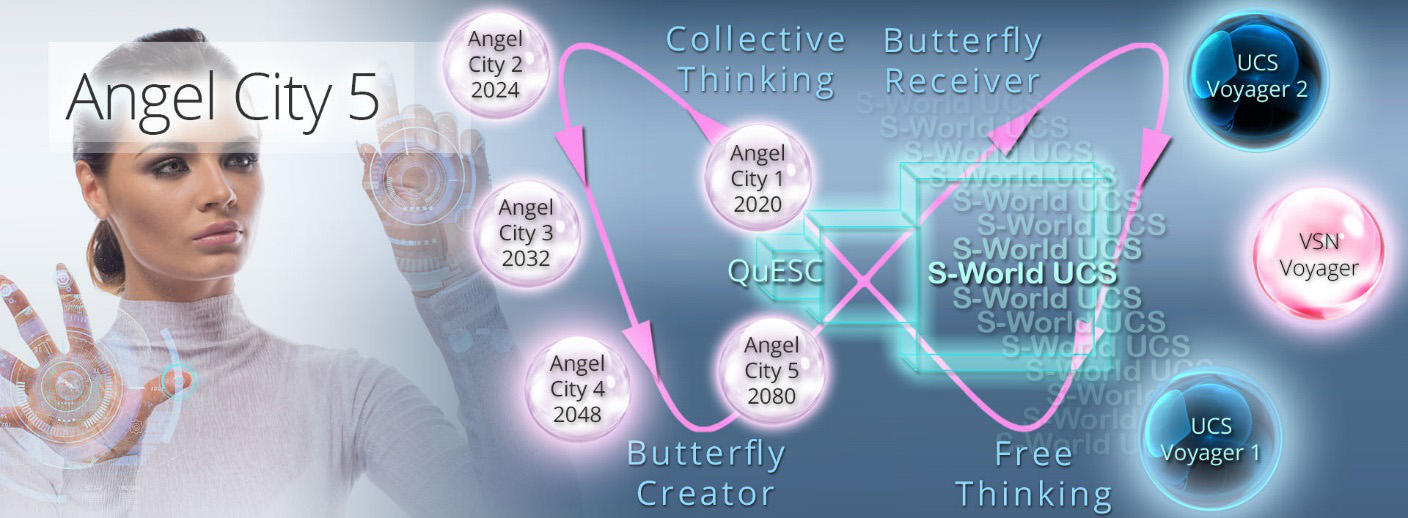
Collectively, Steps 14 and 15 works with the rest of the M-Systems to shape our future per Isaac Asimov’s prescription, that was so pivotal to the development of the network/system back in 2011.

By Isaac Asimov In his words:
“You may not predict what an individual may do, but you can put in motion things that will move the masses in a direction that is desired, thus shaping if not predicting the future.”
This in 2017 is now the purpose of S-World, Angel Theory, M-Systems, and the E-TOE
Next, we add Space

For space, we have an abundance of systems, as the POP cubes (Steps 1 to 6) create (a predicable underlying) financial gravity.
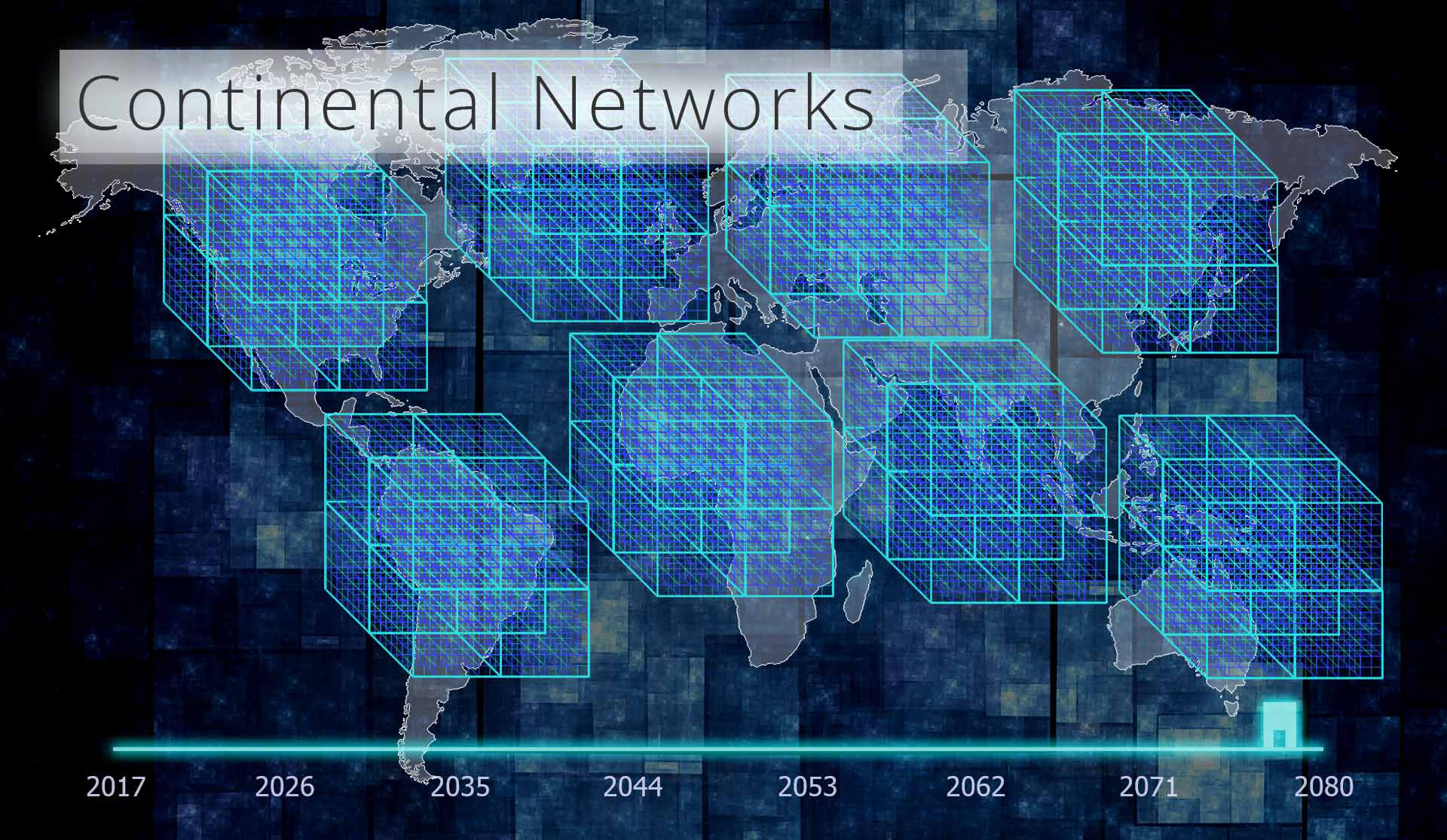
Put the two together and we have space-time.

In terms of special relativity and our time and space being interchangeable, this is our purpose, we wish to create a future prediction, and then guide our ourselves to that future, at which point in time our Angel Cities predictions (our time) and our financial gravity (our space) become one.

Step 16. Part 2: Einstein’s General Relativity

Put simply, Einstein’s theory of general relativity throws away the Newtonian picture of gravity where all objects are attracted to each other, and in its place, presents the idea that gravity is the result of the geometry of existing within a curved space time.
The earth is not attracted to the Sun, instead, the Sun has warped space-time, and the earth is simply moving in a straight line around the warp in space-time created by the sun.
Not unlike placing a heavy bowling ball in the middle of a large trampoline and rolling a marble forward and see it orbit the bowling ball.
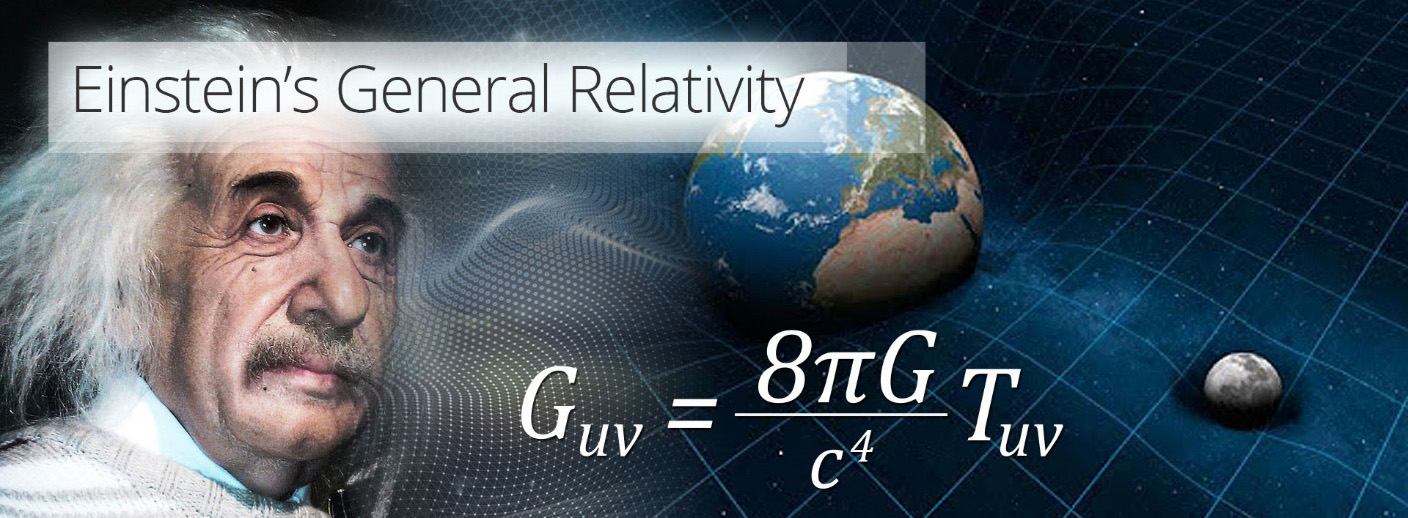
Whilst technically general relativity has proved Newton’s work as not perfect, general relativity only makes a difference at points of high gravity.
For instance, Newton’s equations are all that is needed to land a man or woman on the Moon or Mars. But become slightly inaccurate when it comes to measuring the orbit of the planet Mercury (the planet nearest the sun), and become wholly inaccurate if one were to attempt to measure the gravity of a black hole, a wormhole, or go back to the beginning of time to the big bang.
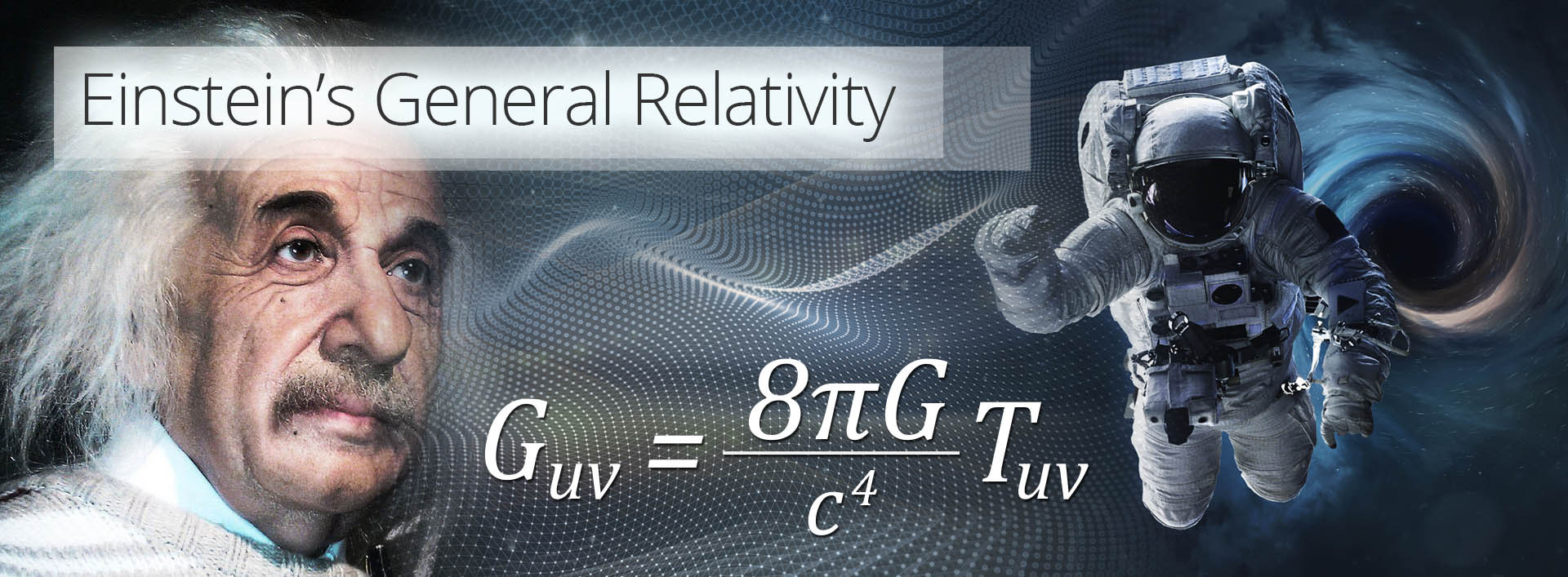
“Einstein’s field equation (see above) uses ‘super-compacted notation’ so, like Dr Who’s Tardis, it is bigger on the inside than on the outside. The left-hand side of the equation is in fact a 4 by 4 table of numbers known as the Einstein curvature tensor, which summarises the curvature of space-time. The right-hand side is another 4 by 4 known as the stress energy tensor, which summarises the sources of gravity.
That Einstein’s equations contain 4 times 4 tables of numbers means that there are actually 16 equations.”
From ‘The Ascent of Gravity’ by Marcus Chown.
That there are 16 equations is an interesting observation for the future. For now the influence on M-Systems from general relativity is that the universe does not sit in a framework of perfect cubes, spacetime is contorted and stretched.
And we shall mimic as follows… Instead of growing evenly (which is the quality of M-System 15. Angel POP), we need to accelerate the locations in abject poverty relative to the richer countries, whilst still making sure richer countries are stable and growing nicely.

Picture a landscape with mountains and valleys; where the mountains represent rich areas and the valleys represent areas of abject poverty. This can become an alternate view of the Global Network Cube. The objective is to grow the mountains and eliminate the valleys, and in general smooth everything out. By 2080 still leaving an uneven landscape with big mountains; but in place of the valleys lie flat areas and hills in some cases, and a much more fare and even economy. Indeed, we can say that general relativity is the flagship of Special Project 5. Equality & The Poverty Gap.
In terms of creating M-Systems, that’s all we have so far for Relativity, and whilst there has not been a specific system that generates more money, we have found ways to look and grow the network differently. We have given more relevance to some systems and, most importantly, I feel we are nicely primed for others to contribute, as it seems we are on the verge of something very exciting popping out of our M-theory simulated economy.

And whilst it is very early days for ‘relativity’ within this simulation, the fact that space time popped out; as soon as we added the quantum time elements is interesting in itself, as it is a step towards Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity popping out of M-theory per Professor Edward Witten’s observation:
“If Einstein had never discovered relativity, it may have been discovered as a by-product of string theory.
General relativity, in some sense, is for free.”

Professor Edward Witten
Winner of the Fields Medal
Charles Simonyi Professor at Princeton University










